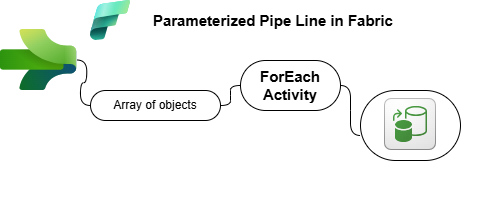
Scenario: Metadata-Driven Data Pipeline in Microsoft Fabric
Your company, DataFlow Inc., needs a scalable and dynamic solution for data movement across multiple sources. Instead of manually configuring multiple Copy Data activities, the team has decided to implement a Metadata-Driven Pipeline (DP003) in Microsoft Fabric, where metadata is passed as an array of objects.
This approach will allow the pipeline to read metadata dynamically at runtime and process multiple data transfers in a single execution.
Project Architecture
Below is the step-by-step breakdown of the project:
Click on + or – to expand or collapse the icon
1️⃣ Creating the Data Pipeline
👉 Fabric Workspace: Create a new Data Pipeline named DP003_MetadataDrivenPipeline.
2️⃣ Storing Metadata in a Parameter
👉 Instead of hardcoding dataset details, create a Pipeline Parameter named DatasetMetadata, with Array type. Use the following JSON structure:
[
{"Source": "addresses.csv", "Destination": "B_Addresses"},
{"Source": "contacts.csv", "Destination": "B_Contacts"},
{"Source": "locations2.csv", "Destination": "B_Locations"},
{"Source": "phones.csv", "Destination": "B_Phones"}
]
We Will pass this Array in Default Value
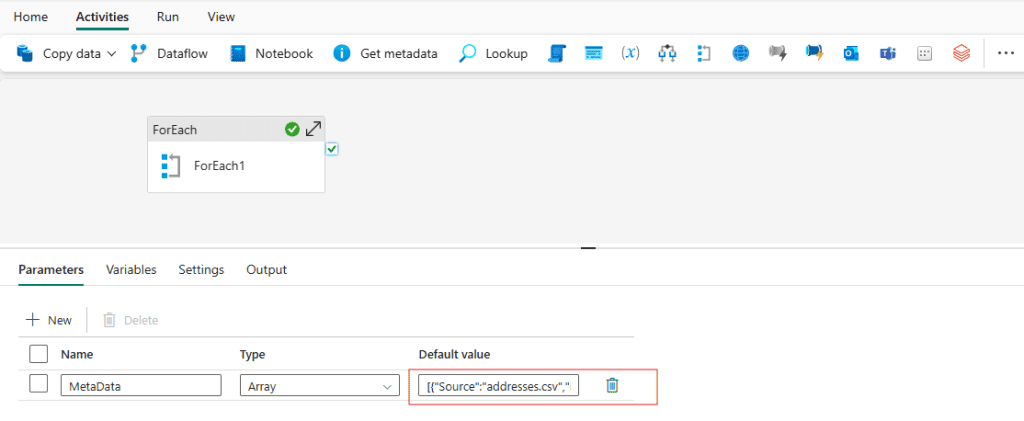
This array of objects acts as a set of instructions for the pipeline to process each dataset dynamically.
3️⃣ Implementing the ForEach Loop
👉 Add a ForEach Activity to iterate through the metadata array.
- Set Items to
@pipeline().parameters.DatasetMetadata
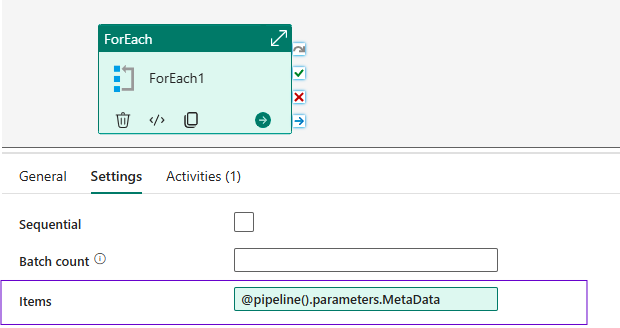
Now this mean for each item of Metadata parameter from default value it will take
- Inside the ForEach loop, add a Copy Data Activity
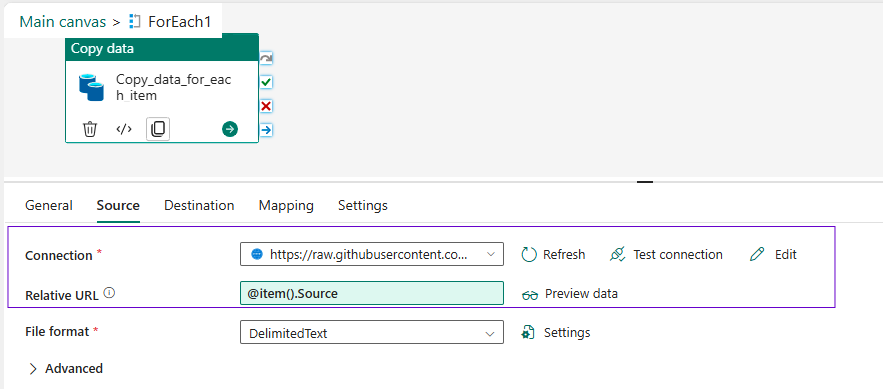
4️⃣ Configuring the Copy Data Activity
👉 Inside the ForEach Activity, configure the Copy Data Activity:
- Source Type: HTTP (Anonymous Connection)
- Base URL: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Fabric/dojo/datasets/ fabric
- Relative URL: Use dynamic content to fetch the correct dataset:
@item().Source
- Destination Type: Fabric Data Warehouse
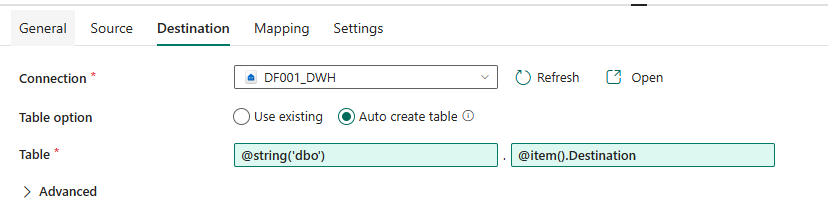
- Table Name: Use dynamic content to assign the correct table name:
@item().Destination - Schema give default dbo (convert it into string)
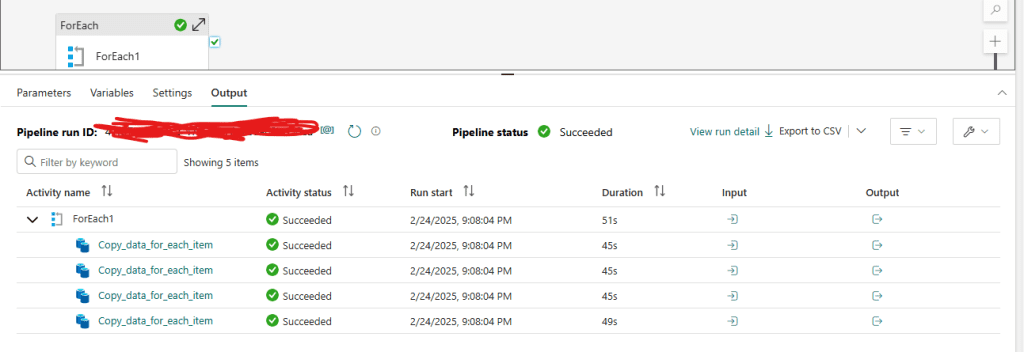
5️⃣ Running & Validating the Pipeline
👉 Execute the pipeline and verify that four new tables are created in your Data Warehouse:
✅ B_Addresses
✅ B_Contacts
✅ B_Locations
✅ B_Phones
Reflection on Learning
Why use Metadata for Pipelines?
- Scalability: Instead of hardcoding multiple Copy Data activities, a single pipeline can handle multiple datasets dynamically.
- Maintainability: Adding new datasets only requires updating metadata instead of modifying the pipeline.
How else could we store Metadata?
- JSON File: Store metadata in a structured JSON file and retrieve it dynamically.
- Metadata Table: Store dataset mappings in a database table and query them at runtime.
How does the Metadata Structure Impact Pipeline Design?
- The array of objects format makes it easy to loop through datasets.
- Dynamic content expressions allow seamless parameterization of source and destination.
Final Thoughts
By using a metadata-driven approach, we have significantly improved the efficiency and scalability of our Fabric Data Pipeline. This method can be extended further by dynamically handling schema changes, error handling, and logging mechanisms.
💡 Next Steps: Explore storing metadata in external files/tables and integrating logging mechanisms!